What is Burke Litwin Model of Change?
W. Warmer Burke and George H. Litwin were two famous organisational change consultants. In 1960s, they developed a model which is known as Burke Litwin Model of Change.
This model identifies three levels of changes in an organisation which are derived by 12 factors or drivers of change.
Among the three levels of change, first is the transformational change which happens due to external environment. It has a direct impact on mission and strategy, leadership, and organizational culture.
Next is the transactional change which affects structure, management practices, system and procedure and working climate. Together with transformational and transactional changes, there is impact on motivational level and individual and organizational performance.
Although there are many factors which affect organisational change. And Burke Litwin Model of Change identifies relationship between level of changes and factors of changes.
Explanation of Burke Litwin Model with Diagram
The middle four factors present the transactional factors. This is about day to day activities which are controlled by relationship by different departments within organization.
The final factors present performance of both individuals and organisation as a whole.
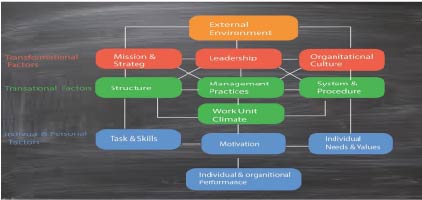
12 factors/elements of Burke Litwin Model
Burke Litwin Model identify 12 factors or elements of change which drive change in an organization.
Let’s check these 12 factors out and discuss these in detail.
01. External environment
The external environment is the set of factors outside an organization that can have a significant impact on its operations, strategies, and performance. These factors may include economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, and economic growth, as well as changes in competition, technology, and regulations.
For example, changes in consumer preferences and behaviors can alter demand for products and services, while advancements in technology can create new opportunities and challenges for the organization. Understanding and adapting to the external environment is critical for organizations to maintain their competitive edge and achieve long-term success.
02. Mission and strategy
Mission and strategy are important elements in the Burke-Litwin model of change management. The mission represents the organization’s purpose, values, and direction, while the strategy defines the plan of action for achieving the mission. A well-defined mission and strategy provide clarity and direction to the organization, helping to align its goals, objectives, and resources.
A clear mission statement can help employees understand the organization’s purpose, and how their work contributes to achieving its goals. A well-crafted strategy can help the organization identify and prioritize its actions, allocate resources effectively, and measure its performance. In essence, mission and strategy define the “what” and “how” of the organization, respectively, and are essential components for effective organizational change and long-term success.
03. Leadership
There is a strong link between successful change management and leadership. Effective leadership is critical for achieving organizational goals, building a positive work environment, and managing change. Leaders play a key role in setting the organization’s direction, communicating its vision and values, and creating a culture that supports the achievement of its mission and strategy.
Effective leadership involves not only providing direction but also empowering employees to take ownership of their work, develop their skills, and contribute to the organization’s success. Thus, understanding and developing effective leadership is a critical element in the management of change and achieving long-term success.
04. Organisational culture
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors that define the identity and character of an organization. Organizational culture plays a significant role in shaping how employees perceive and experience their work environment, their sense of belonging, and their level of commitment to the organization’s mission and goals.
Organizational culture is an essential factor to consider when managing change in an organization. When initiating a change, it is important to assess the existing culture and ensure that the change is aligned with the organization’s values and beliefs. It is also critical to ensure that the change is communicated effectively and that the new culture is actively promoted and reinforced. By understanding and managing organizational culture, an organization can improve employee satisfaction, engagement, and performance, which can lead to long-term success.
05. Structure
Structure refers to the formal and informal relationships, roles, and responsibilities among employees, departments, and teams within an organization. Organizational structure can be hierarchical or flat, centralized or decentralized, and can have different functional or product-based divisions.
When managing change, it is essential to consider the impact of the proposed changes on the organization’s structure. Changes in strategy or new initiatives may require changes in the structure to ensure that the organization is aligned and equipped to implement them successfully. For example, introducing new products or services may require creating new product-based teams or divisions. Similarly, a merger or acquisition may require a new structure that incorporates the new organization and its employees.
06. Systems
The “system” element in the Burke-Litwin model of change management refers to the set of processes, procedures, and routines that an organization uses to achieve its goals. This element encompasses the various systems that support an organization’s operations, including its technology, information systems, financial systems, performance management systems, and others.
The systems element is critical to an organization’s success as it affects how work is performed, how data is collected and analyzed, and how decisions are made. Well-designed systems can improve efficiency, quality, and decision-making, while poorly designed systems can create inefficiencies, errors, and confusion.
07. Management practice
Management practices refers to the management processes and procedures that an organization uses to plan, organize, direct, and control its resources to achieve its goals. Management practices can include human resource management, financial management, strategic planning, performance management, and other management functions.
Effective management practices are essential for achieving an organization’s mission and goals, managing change, and ensuring the long-term success of the organization. Management practices can impact employee satisfaction, productivity, and performance, and they can also impact an organization’s ability to respond to internal and external changes.
08. Working climate
Work climate refers to the attitudes, perceptions, and feelings of employees towards their work environment, including their job satisfaction, motivation, and engagement.
A positive work climate is one where employees feel supported, valued, and engaged in their work. A negative work climate, on the other hand, can lead to low morale, high turnover, and decreased productivity.
When managing change, it is important to consider the impact of the proposed changes on the work climate. Changes that are perceived as positive by employees can lead to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and engagement. Conversely, changes that are perceived as negative can lead to decreased job satisfaction and increased resistance to change.
09. Tasks and skills
Tasks and skills refers to the tasks and skills required to perform the work of an organization. This element includes the job duties and responsibilities of employees, the skills and knowledge required to perform those duties, and the training and development programs needed to enhance those skills.
To manage tasks and skills during a change initiative, it is important to identify the skills required to implement the change successfully and ensure that employees have the necessary training and development programs to acquire those skills. Providing opportunities for employees to learn and develop new skills can also help to create a positive work climate and increase employee engagement
10. Individual values and needs
Individual values and needs refers to the values, beliefs, and needs of individuals within the organization, and how these factors influence their behavior and performance.
Individual values and needs can impact employee motivation, job satisfaction, and engagement, and can also influence how employees respond to change initiatives. For example, employees who value job security and stability may be resistant to changes that they perceive as threatening to their job security.
By understanding the values and needs of employees and addressing their concerns and perceptions, an organization can create a positive work environment that supports successful change initiatives.
11. Motivational level
Motivational level refers to the level of motivation and commitment that employees have towards achieving the goals of the organization. Motivation is the internal drive that determines the level of effort and persistence that an employee puts into their work.
To manage motivational level during a change initiative, it is important to communicate the reasons for the change and the benefits to the organization and its employees. Providing opportunities for employees to provide feedback and participate in the change process can also help to create a positive work climate and increase engagement.
12. Individual and organizational performance
Performance of individuals refers to completion of tasks in effective and efficient manner. And sum total of individual performance is the organizational performance.
Performance can be measured by various metrics, such as productivity, efficiency, quality, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
Changes that are aligned with the goals and objectives of the organization can lead to improved performance, while changes that are misaligned or poorly implemented can lead to decreased performance.
Why to use Burke Litwin Model of Change /Advantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change.
- This is a comprehensive model covers all the important factors into account to explain why change is happening, what is driving change and helps in formulating change strategy.
- This model explains factors of change on the basis of cause and effect relationship which helps to have complete understanding about organizational change.
- This model explains the meaning and distinction between transformational and transactional level of change leadership in an organization.
Limitations and Disadvantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change
- The critics of this model are of the view that over simplification of different factors of change results into producing sub factors which actually makes it a more complex model.
- This model only focuses on what drives change and fail to explain how to implement change.
- It puts external environment factors on the top which drives change which is not always the case. There are internal factor as powerful factors which lead to organizational change.
Take Home Points:
- Burke Litwin Model of Change explains three levels of changes- transformational, transactional changes and changes in performance.
- These changes are derived by 12 factors which include external environment, mission and strategy, leadership, organizational culture, structure, system, management practices, working climate, task and skills, individual values and needs, motivation level and individual and organizational performance.
- Among these drivers some are hard factors and some are soft; some are tangible and some are intangible.
- Organizational change is a display of these complex yet interconnected factors of change.



