What is Kubler Ross Change Curve?
Have you ever experienced a traumatic situation like death of your loved one or any sort of distressing crisis at work place?
These are extremely difficult situations to cope with for any human being. A response by human to such situations is explained by a Swiss psychiatric Elisabeth Kubler Ross who developed a model which is also widely known Kubler-Ross Change Curve or 5 Stages of Grief and Loss.
Kubler-Ross undertook research on the subject of death and experience of dying; and worked with patients who were terminally ill in different hospitals. She analyzed and evaluated hundreds and thousands of patients to complete her research.
Finally, she came up with 5 Stages of Grief and Loss which was published in her book in 1969 titled Death and Dying. These five stages represent a series of emotions a person gone through after experiencing traumatic situation.
Although the stages of grief or loss is explained from individuals who are ill or under extreme depression; yet this model holds true for other situations like work, employment and business.
This model has been widely accepted and applied to broadly explain the process of change because the emotions are the same whether it’s about personal loss or changes happening in organizations.
Let’s dig deeper into what are 5 Stages of Grief and Loss or Kubler-Ross Change Curve.
Stage 1: Shock or Denial
Shock is the first response to hearing a bad news. And a person immediately goes into a state of denial and tends to think that this news is not correct.
He says like this can not be happened to him. Some persons recover early and some remain stuck in this state for a long time and do not accept reality.
Same is true for employees who come to know that change is happening in their organization and their jobs would be at risk. They don’t accept realities and deny the new situation. They need some time to adjust to change.
How to manage this stage? This stage demands careful communication on the part of employer and change leaders. It is necessary to share only relevant information and avoid the irrelevant details which may cause panic among the employees.
Stage 2: Anger
Anger is the next response when someone is unable to reverse the fact or reality. When someone feels powerless then he/she starts blaming others. In this situation a person tends to think like why this is happening to him/her or this is not fair.
At organizations or work, after initial shock about change hit employees then they become angry.
Their resentment or anger is directed towards themselves and it may be towards others colleagues. The employees tend to think without reason and express their frustration all the time.
How to manage this stage? The management should expect this sort of behavior from affected employees. It is just a natural response and may be fade away with time. It is the management who should stay calm; and communicate clearly and logically to manage this situation.
Stage 3: Bargaining
A person starts to bargain or negotiate with the dreadful realities when the impact of bad news begins fading away. He starts thinking how to live with ugly facts. He wants some more time to delay the new situation. He/she tends to think like what if I do this? and can I get some more time?
In work environment, he/she wants to continue working for some time. Basically, employee tries to find ways to postpone the emerging change. They need little adjustments to find new ways to manage the situation.
How to manage this stage? The management should show flexibility and be open to suggestions to make employees move forward. This will surely bring some relief to the affected employees. However, the management should tactfully make employee learn about the expectation from the emerging situation.
Stage 4: Depression
Depression is the stage when a person feels sadness, regret, guilt and completely helpless. He gives up and becomes isolated. He avoids meeting other people around.
He/she sometimes might take refuge in drugs. He loses all positive energy and feels all time negative for him/herself and for others as well.
In work environment, employee feels he is locked in a dead-end and nothing is going to happen in his/he favor. He/she has no interest at all in his/her work and works with lowest energy. He loses trust of everyone including his/her colleague and management.
How to manage this stage? It is important for management to understand that this is the hardest phase for employees. In this stage, they need to be taken care of and listened. The management can come up with positive actions like rewards, more exciting training and workshops for the new roles and responsibilities.
Stage 5: Acceptance
When a person is sure that there is no more hope then he tends to accept the fact or loss. This helps him/her to recover from the previous stage and have reconciliation with the reality. This acceptance helps to resume his/her to life.
As for employees who are suffering grief due to change happening in organization, this is the stage when he/she accepts change embrace new role and responsibilities. He/she becomes terms to change and ready to move forward on journey to change.
How to manage this stage? The management finally feels relaxed that its employees have accepted the new realities. It will improve productivity and also progress towards the big goal. The management needs to reinforce the purpose of change and improve the strategy based on the learnings from the previous stages.
The Change Curve
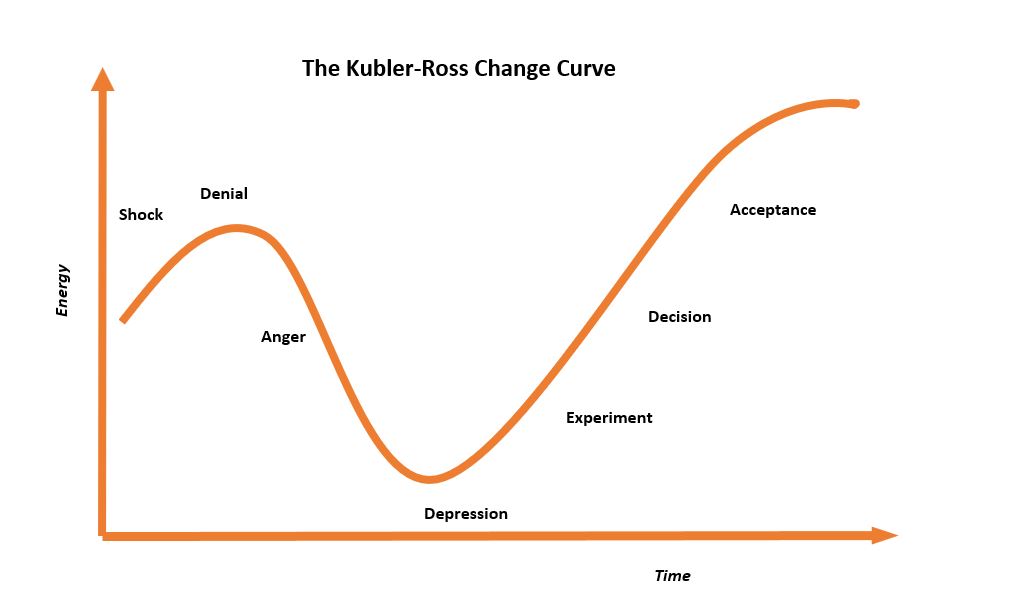
The Change Curve is a tool which can be used to know what is emotional stage of employees and where they are on their transitional journey with regard to change happening in their work environment.
This helps the management to manage the situation through effective communication and other methods to support and guide their human resource on the journey of change.
The Change Curve starts with shock and denial and it dips down at anger stage and touches the lowest energy when curve reaches at the stage of depression.
As the time passes by, the curve begins to go upward and regain energy level till the highest point which is the stage of acceptance.
Advantages of Kubler-Ross Change Curve
Some of the advantages of using this model to understand and manage change include:
- Predictability: The model provides a predictable framework for how people react to change, which can help managers and leaders anticipate and manage the challenges that come with change.
- Communication: The model provides a common language for discussing and understanding the emotional responses to change, which can facilitate communication and collaboration.
- Empathy: The model can help leaders and managers empathize with employees who are struggling with change, which can lead to more effective support and guidance.
- Awareness: The model can help individuals become aware of their own emotional responses to change and understand that these responses are normal and part of the change process.
- Preparation: The model can help individuals and organizations prepare for change by anticipating the emotional responses that may occur and planning accordingly.
- Resilience: By recognizing and addressing the emotional responses to change, the model can help individuals and organizations become more resilient and better equipped to manage future changes.
Disadvantages of Kubler-Ross Change Curve
While the change curve model can be useful for understanding and managing change, there are also some potential disadvantages to be aware of:
- Simplification: The model is often criticized for oversimplifying the complex emotional responses to change. In reality, people may experience a range of emotions that don’t neatly fit into the five stages of the model.
- Linearity: The model suggests that people progress through the stages in a linear fashion, but in reality, people may move back and forth between stages or skip stages altogether.
- Universality: The model assumes that everyone will experience the same emotional responses to change, regardless of the individual or the situation. However, people may have different coping mechanisms and emotional responses based on their personality, cultural background, or previous experiences.
- Timeframe: The model doesn’t account for individual differences in the length of time it takes to move through the stages. Some people may progress through the stages quickly, while others may linger in one stage for an extended period.
- Inability to provide solutions: The model does not provide solutions or actionable steps for addressing the emotional responses to change, which can leave individuals and organizations feeling stuck.
- Limited Scope: The model only focuses on the emotional responses to change and does not address other important factors that can impact successful change management, such as communication, leadership, and planning.
Take Home Points
- Kubler Ross studied terminally ill patients and developed a 5 stages of grief and loss to explain emotional transitions an individual face experiencing catastrophic loss.
- This model is successfully applied to business and work environment to explain behavior of employees going through change process at their organizations.
- The first stage is shock or denial when no body accepts new realities; then comes the stage of anger when employees reacts on what is happening; next stage is bargaining when they think they need some time to delay change.
- The fourth stage is depression which he surrenders and becomes extremely sad with lowest energy and productivity and the last stage is of acceptance when employees embrace change and find ways and solution to adjust in the new situation.
- This simple but important model helps management to understand the emotional reaction of their employees while taking journey towards change and also prepare strategy how organization should handle this situation and what should be responses to each of transitional stage.



